Long term potentiation ap psychology – Long term potentiation (LTP) in AP psychology is a captivating phenomenon that unlocks the secrets of memory formation and learning. It’s a dance between neurons, where repeated stimulation strengthens their connections, leaving a lasting imprint on our brains. Join us as we delve into the molecular mechanisms, induction protocols, and profound implications of LTP in shaping our cognitive abilities.
As we explore the intricacies of LTP, we’ll uncover its crucial role in encoding, storing, and retrieving memories. We’ll also examine its significance in learning and development, shedding light on how we acquire new skills and knowledge. Moreover, we’ll delve into the potential connections between LTP and neurological disorders, seeking insights into their complexities.
Definition and Overview of Long-Term Potentiation
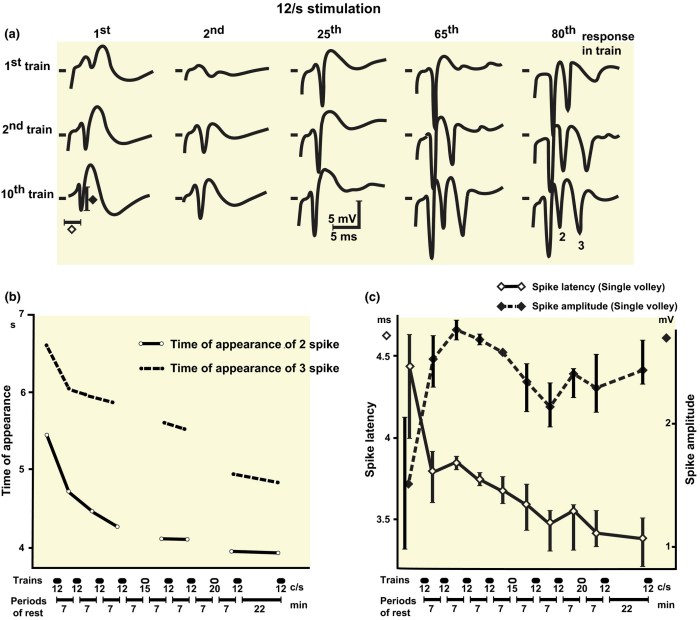
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a persistent increase in synaptic strength that occurs over time as a result of high-frequency electrical stimulation of a synapse. It is widely believed to be the cellular mechanism underlying memory formation and learning.
The molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying LTP are complex and still not fully understood. However, it is known that LTP involves changes in the structure and function of the postsynaptic neuron, including the insertion of new AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane and the phosphorylation of existing AMPA receptors.
Synaptic Plasticity and LTP
LTP is a form of synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of synapses to change their strength in response to changes in their activity. Synaptic plasticity is essential for learning and memory, as it allows the brain to store new information and to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Role of LTP in Memory Formation
LTP is believed to play a key role in memory formation. When a synapse is repeatedly stimulated, LTP is triggered, which strengthens the synapse and makes it more likely to fire in the future. This strengthening of synapses is thought to be the physical basis for the storage of memories.
Evidence for the Role of LTP in Memory Formation
There is a great deal of evidence to support the role of LTP in memory formation. For example, studies have shown that LTP can be induced in the hippocampus, a brain region that is known to be involved in memory formation.
Additionally, studies have shown that blocking LTP impairs memory formation.
Induction and Maintenance of LTP
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a form of synaptic plasticity that involves a long-lasting increase in the strength of a synapse following high-frequency stimulation. The induction of LTP is dependent on the activation of NMDA receptors and the subsequent influx of calcium ions into the postsynaptic neuron.
This calcium influx triggers a cascade of molecular events that ultimately lead to the strengthening of the synapse.
Induction of LTP
LTP can be induced using various protocols, including:
-
-*High-frequency stimulation (HFS)
This is the most common method of inducing LTP. It involves delivering a train of high-frequency electrical pulses to the presynaptic neuron.
-*Theta-burst stimulation (TBS)
This protocol involves delivering a series of brief bursts of high-frequency stimulation. TBS is thought to be more effective at inducing LTP than HFS.
-*Chemical induction
LTP can also be induced by applying chemicals that activate NMDA receptors, such as NMDA or glycine.
Role of NMDA Receptors and Calcium Influx
The induction of LTP is critically dependent on the activation of NMDA receptors. NMDA receptors are glutamate-gated ion channels that are permeable to calcium ions. When NMDA receptors are activated, they allow calcium ions to enter the postsynaptic neuron. This calcium influx triggers a cascade of molecular events that ultimately lead to the strengthening of the synapse.
Maintenance of LTP
Once LTP has been induced, it can be maintained for long periods of time. The molecular mechanisms involved in LTP maintenance are not fully understood, but they are thought to involve changes in gene expression and protein synthesis. These changes lead to the formation of new synaptic connections and the strengthening of existing ones.
LTP and Memory Formation
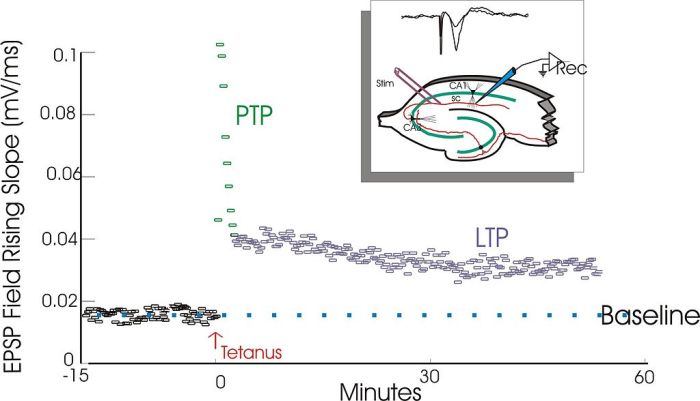
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a cellular mechanism that underlies the formation of memories. Evidence supporting the role of LTP in memory formation includes:
- LTP is induced in the hippocampus, a brain region known to be involved in memory formation.
- The magnitude of LTP is correlated with the strength of memory.
- Blocking LTP impairs memory formation.
LTP contributes to the encoding, storage, and retrieval of memories by:
- Encoding:LTP strengthens synaptic connections between neurons that encode memories.
- Storage:LTP maintains the strength of these synaptic connections over time, allowing memories to be stored.
- Retrieval:LTP facilitates the reactivation of these synaptic connections during memory retrieval.
Limitations of the LTP Hypothesis of Memory
While the LTP hypothesis of memory provides a strong framework for understanding the cellular basis of memory formation, it has some limitations:
- It does not explain all types of memory, such as implicit memory.
- It does not fully account for the complexity of memory processes, such as the influence of context and emotions.
- It does not explain how memories are organized and retrieved.
LTP and Learning and Development
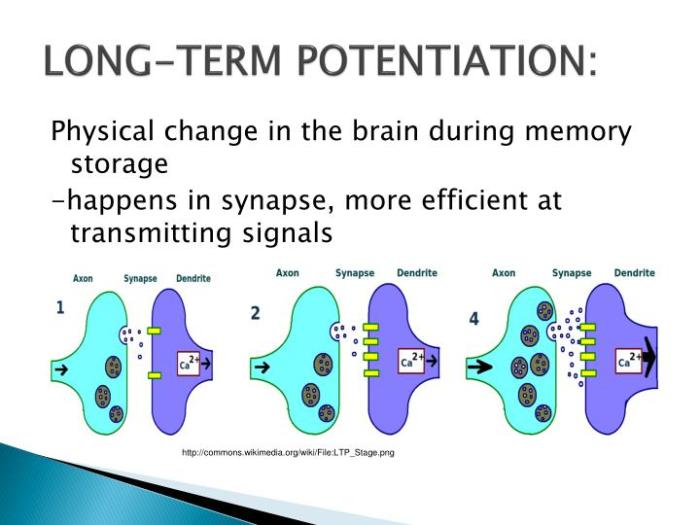
Long-term potentiation (LTP) plays a pivotal role in the processes of learning and development. LTP is a fundamental mechanism by which the strength of synaptic connections between neurons is enhanced over time, resulting in improved signal transmission and enhanced neural processing.
In the context of learning, LTP contributes significantly to the acquisition and consolidation of new skills, knowledge, and memories.
LTP and Skill Acquisition
During the acquisition of new skills, LTP is instrumental in establishing and strengthening neural pathways associated with the specific skill being learned. As an individual repeatedly engages in a particular activity or task, the synaptic connections involved in processing the associated information undergo LTP, leading to an increase in synaptic strength.
This enhanced synaptic strength facilitates more efficient transmission of signals, enabling the individual to perform the skill with greater accuracy and proficiency over time.
LTP and Knowledge Acquisition
LTP is also essential for the acquisition of new knowledge. When new information is encountered, LTP facilitates the formation of new synaptic connections between neurons involved in processing and storing the information. The strengthening of these connections through LTP ensures that the new knowledge can be effectively encoded and retrieved later when needed.
This process underlies the ability to learn and remember facts, concepts, and ideas.
Implications for Educational Practices
The understanding of LTP and its role in learning and development has significant implications for educational practices. By leveraging the principles of LTP, educators can design teaching strategies that promote the development of strong and lasting neural connections in students’ brains.
This can be achieved through methods such as spaced repetition, interleaving, and retrieval practice, all of which have been shown to enhance LTP and improve learning outcomes.
LTP and Neurological Disorders
Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a crucial process in learning and memory formation. However, recent research suggests that LTP may also play a role in the development and progression of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and schizophrenia.
Alzheimer’s Disease
In Alzheimer’s disease, there is a progressive loss of synapses and neurons, particularly in the hippocampus, a brain region critical for memory formation. Studies have shown that LTP is impaired in the hippocampus of Alzheimer’s patients, suggesting that disruptions in LTP may contribute to the memory deficits characteristic of the disease.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and cognitive impairments. Research has found that individuals with schizophrenia have altered LTP in specific brain regions, such as the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in higher-order cognitive functions. These LTP abnormalities may contribute to the cognitive deficits and altered brain connectivity observed in schizophrenia.
Therapeutic Strategies, Long term potentiation ap psychology
Given the potential role of LTP in neurological disorders, researchers are exploring therapeutic strategies that target LTP to treat these conditions. One approach involves using drugs that enhance or inhibit LTP, with the aim of restoring normal LTP function in affected brain regions.
FAQs: Long Term Potentiation Ap Psychology
What is the role of NMDA receptors in LTP?
NMDA receptors play a critical role in LTP induction. When activated by glutamate, they allow calcium ions to enter the neuron, triggering a cascade of events that lead to the strengthening of synaptic connections.
How does LTP contribute to memory formation?
LTP is believed to be a cellular mechanism underlying memory formation. The strengthening of synaptic connections associated with LTP allows for more efficient transmission of signals between neurons, which is thought to represent the storage of memories.
What are the potential therapeutic implications of targeting LTP for neurological disorders?
Targeting LTP may offer therapeutic potential for neurological disorders characterized by cognitive impairments. By modulating LTP, researchers aim to restore or enhance synaptic plasticity, potentially improving memory function in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.