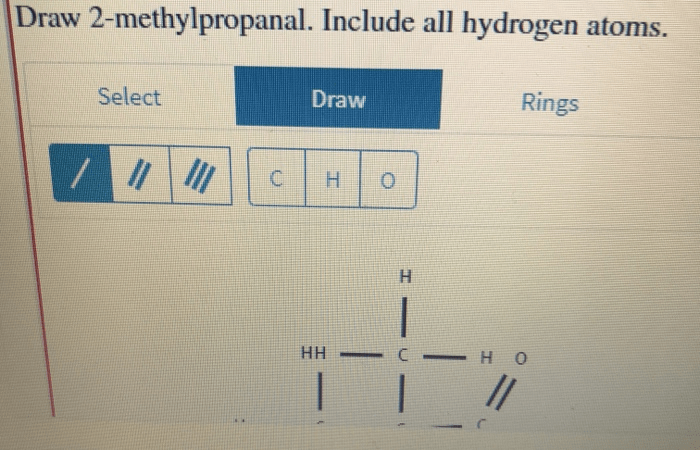
Draw 2-methylpropanal. Include all hydrogen atoms. This seemingly simple task requires a deep understanding of structural formula and molecular geometry. Delve into this comprehensive guide to master the art of representing this organic compound accurately.
2-Methylpropanal, also known as isobutyraldehyde, is a branched-chain aldehyde with the molecular formula C4H8O. Its structural formula depicts a central carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to two methyl groups and a hydrogen atom. Understanding the molecular geometry of 2-methylpropanal is crucial for predicting its physical and chemical properties.
2-Methylpropanal
-methylpropanal, also known as isobutyraldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCHO. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is a structural isomer of butanal.
Structural Formula
The structural formula of 2-methylpropanal is:“` O || CH3-C-CH2-CH3“`The molecule consists of a central carbon atom bonded to a methyl group (-CH3), a methylene group (-CH2-), and a carbonyl group (-CHO). The methyl group and the methylene group are both attached to the central carbon atom by single bonds, while the carbonyl group is attached by a double bond.
Molecular Geometry, Draw 2-methylpropanal. include all hydrogen atoms
The molecular geometry of 2-methylpropanal is trigonal planar around the central carbon atom. This is because the central carbon atom has three electron groups around it: the two methyl groups and the carbonyl group. The electron groups repel each other, causing the molecule to adopt a trigonal planar geometry.
Functional Groups
-methylpropanal contains two functional groups: a methyl group and a carbonyl group. The methyl group is a hydrocarbon group consisting of a carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms. The carbonyl group is a functional group consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
Isomerism
-methylpropanal exhibits structural isomerism. Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. The structural isomer of 2-methylpropanal is butanal. Butanal has the molecular formula CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Nomenclature
The IUPAC nomenclature of 2-methylpropanal is 2-methylpropanal. The name is derived from the following rules:
- The base name of the compound is propane.
- The prefix “methyl” indicates that there is a methyl group attached to the propane chain.
- The suffix “-al” indicates that the compound is an aldehyde.
The common name of 2-methylpropanal is isobutyraldehyde.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- -methylpropanal is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It has a boiling point of 102 °C and a density of 0.80 g/mL. It is soluble in water and organic solvents.
- -methylpropanal is a reactive compound. It undergoes a variety of reactions, including nucleophilic addition, oxidation, and reduction.
Preparation
- -methylpropanal can be prepared by a variety of methods, including:
- The oxidation of 2-methylpropanol.
- The hydration of isobutylene.
- The hydroformylation of propene.
Reactions
-methylpropanal undergoes a variety of reactions, including:
Nucleophilic addition
2-methylpropanal can undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with a variety of nucleophiles, including water, alcohols, and amines.
Oxidation
2-methylpropanal can be oxidized to form 2-methylpropanoic acid.
Reduction
2-methylpropanal can be reduced to form 2-methylpropanol.
Applications
-methylpropanal is used as a solvent, an intermediate in chemical synthesis, and a starting material for other compounds. It is also used in the production of fragrances, flavors, and pharmaceuticals.
User Queries: Draw 2-methylpropanal. Include All Hydrogen Atoms
What is the IUPAC name of 2-methylpropanal?
The IUPAC name of 2-methylpropanal is 2-methylpropanal.
What is the molecular weight of 2-methylpropanal?
The molecular weight of 2-methylpropanal is 72.11 g/mol.
What is the boiling point of 2-methylpropanal?
The boiling point of 2-methylpropanal is 63-64 °C.