Mixed ionic/covalent compound naming answer key – Welcome to the definitive guide on mixed ionic/covalent compound naming, your key to understanding the intricacies of chemical nomenclature. This answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the rules and conventions for naming these compounds, ensuring accurate and consistent communication within the scientific community.
As we delve into the fascinating world of mixed ionic/covalent compounds, we will explore their unique characteristics, delve into their oxidation states, uncover the secrets of their Lewis structures, and unravel the properties that govern their behavior. This journey will empower you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the complexities of chemical nomenclature with ease.
Mixed Ionic/Covalent Compound Nomenclature: Mixed Ionic/covalent Compound Naming Answer Key
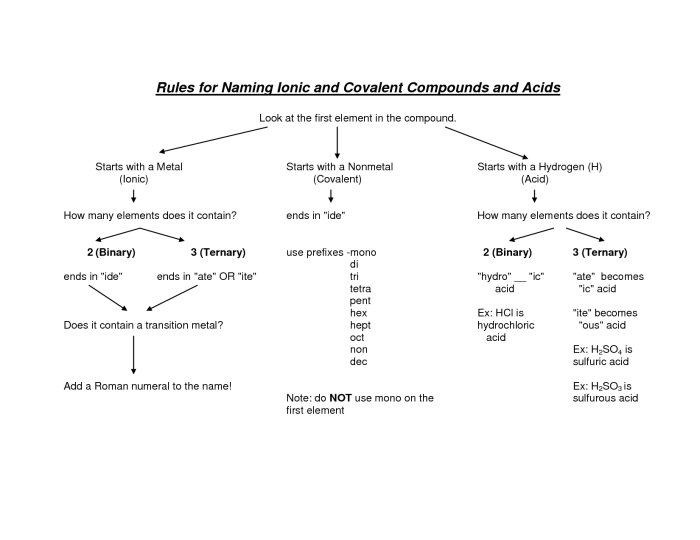
Mixed ionic/covalent compounds are compounds that contain both ionic and covalent bonds. They are typically formed between a metal and a nonmetal, with the metal losing one or more electrons to the nonmetal.
To name a mixed ionic/covalent compound, we first need to determine the oxidation states of the elements involved. The oxidation state of an element is the charge it would have if all of its bonds were ionic. Once we know the oxidation states, we can use the following rules to name the compound:
- The cation (positive ion) is named first, followed by the anion (negative ion).
- The name of the cation is the same as the name of the element.
- The name of the anion is the root of the element’s name, followed by the suffix “-ide”.
- If the metal is in a variable oxidation state, the oxidation state is indicated by a Roman numeral in parentheses after the name of the metal.
Here are some examples of mixed ionic/covalent compounds and their names:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium oxide (K 2O)
- Calcium fluoride (CaF 2)
- Iron(III) oxide (Fe 2O 3)
- Copper(II) sulfate (CuSO 4)
Quick FAQs
What are mixed ionic/covalent compounds?
Mixed ionic/covalent compounds are chemical compounds that exhibit both ionic and covalent bonding characteristics.
How do you determine the oxidation states of elements in mixed ionic/covalent compounds?
Oxidation states can be determined using various methods, including the oxidation number method and the half-reaction method.
What is the significance of Lewis structures in understanding mixed ionic/covalent compounds?
Lewis structures provide a visual representation of the electron distribution within a molecule, helping to identify ionic and covalent bonds and predict molecular geometry.